How To Use Network Utility on Mac
macOS includes an application called Network Utility. This means that you do not need to download or install this app. This app provides a variety of handy networking tools and details. You can use this tool for variety of purposes, from troubleshooting a connection to looking up information.
How to find Network Utility:
There are two ways to open Network Utility.
The official path for the app is:
/System/Library/CoreServices/Applications
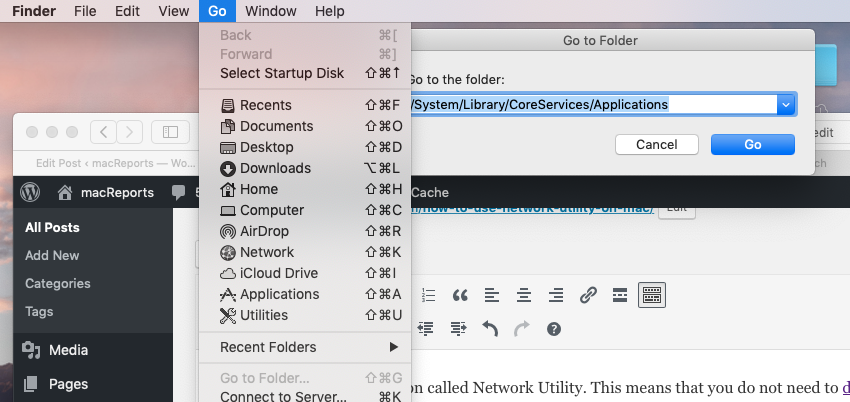
To open this folder, go to Finder, and click Go and Go To Folder and enter the path above and hit Go:
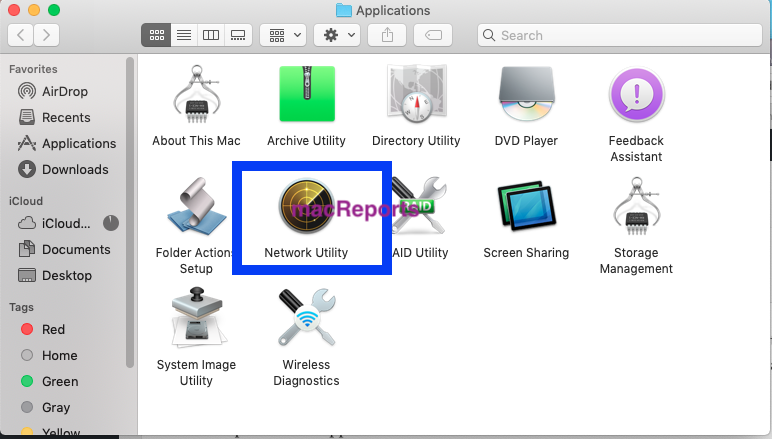
And then click Network Utility
If you are running an older version of macOS (OS X Mountain Lion, Lion, and Snow Leopard), then go to Finder> Applications > Utilities.
You can also open Spotlight by pressing Command-Space bar and type Network Utility to search and launch this app.
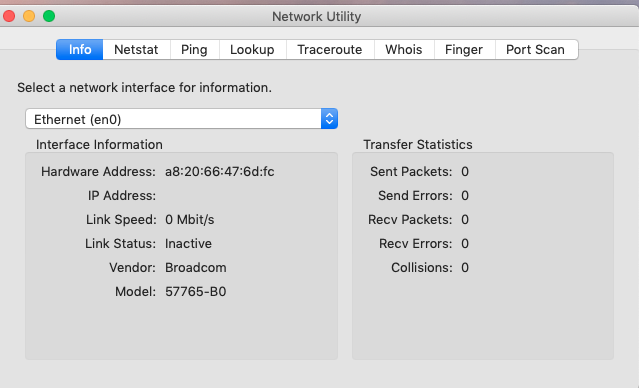
Network Utility lets you view information about your network connections:
The followings are the tools included in Network Utility.
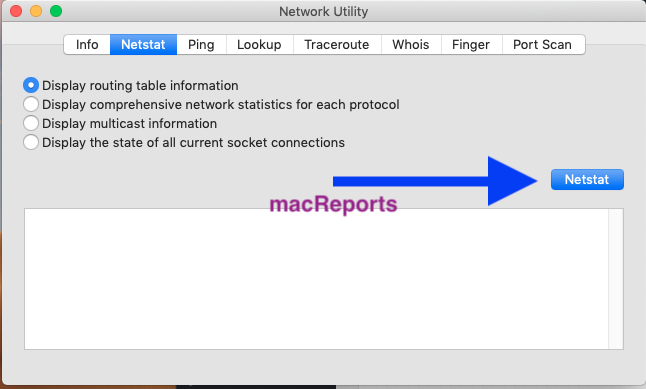
Netstat: This means Network Statistics. You can use this tool to display very detailed information about all the active network connections (incoming and outgoing) on your Mac.
There are four options here and they are:
- Display routing table information
- Display comprehensive network statistics for each protocol
- Display multicast information
- Display the state of all current socket connections
You need to select one, and then click the blue “Netstat” button:
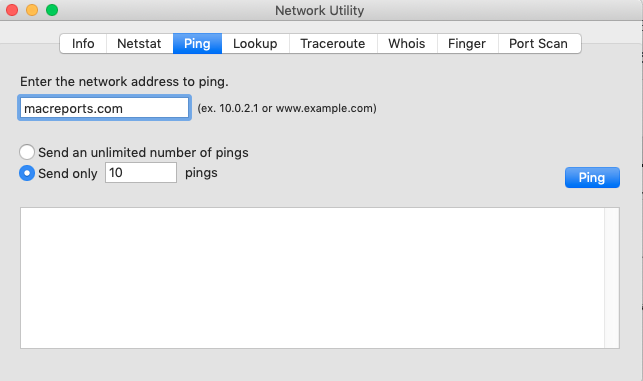
Ping: This tool lets you test the reachability of your Mac on an Internet Protocol (IP) network.
You need to enter an IP number (like 10.0.2.1) or URL (like macreports.com). You have also the option of sending only a selected number (like 10) of pings or unlimited number of pings. And then click the yellow Ping button:
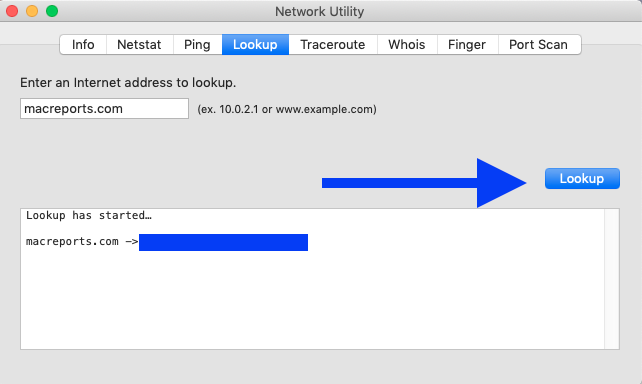
Lookup: This tool will let you test your DNS server. Simply enter an Internet address and then click Lookup.
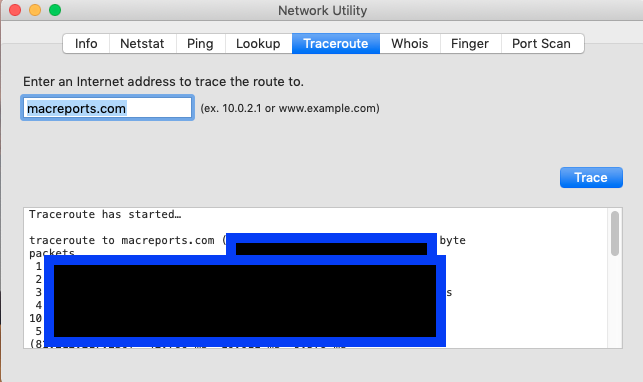
Traceroute: This will let you trace network traffic paths.
Simply enter the IP address or domain name and click Trace. It may take up to a minute for the results.
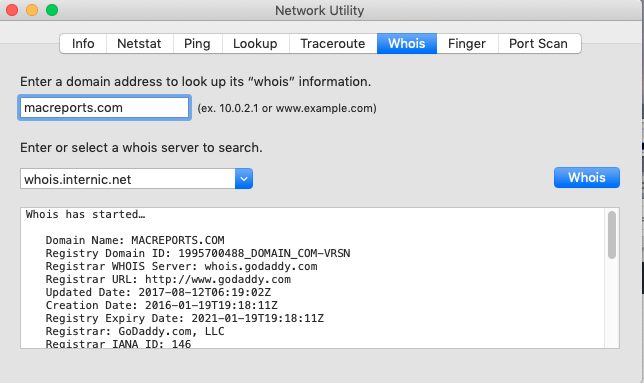
Whois: You check a domain’s whois information. This will let you review the ownership and tenure of a domain name. So you can review who registered and owns a domain name, including their contact information. Simply enter a domain name address and and then select a whois server to search. Then click Whois.
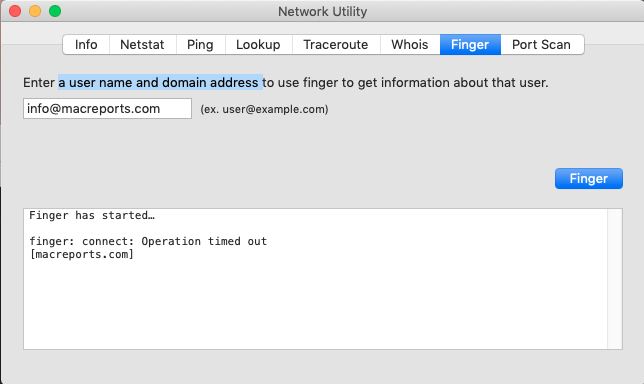
Finger: You can use this to find information about computer users. Simply enter a username and domain address to do this test:
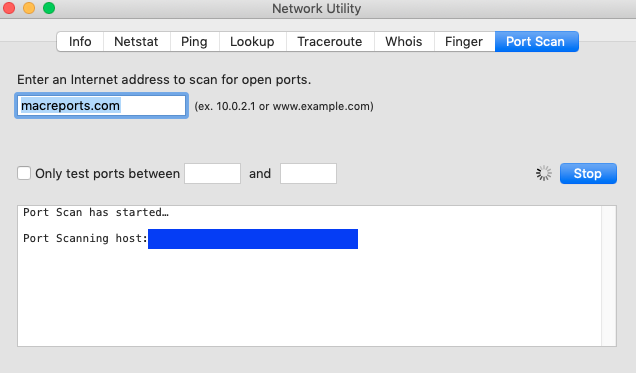
Port Scan: This tool will let you check for open TCP/IP ports, ports 1 through 65535. Simply enter an Internet address to do this test:
Your Mac’s Network Utility is a basic but offers handy networking tools.