How to Turn on and Use SSH and SFTP on Mac
You can access your Mac remotely from another computer using SSH or SFTP. SSH stands for Secure Shell, which allows a secure way to access and manage remote devices over an unsecured network. SFTP stands for SSH File Transfer Protocol, which is a secure method for transferring files between computers over a network.
SSH and SFTP are used to establish a secure network connection between computers to run commands or transfer files remotely as if you were sitting in front of the other computer. macOS has a built-in SSH client that you can use in Terminal. This feature is called Remote Login on Mac. By default, it is disabled. In this article, I’ll go over how you can turn on Remote Login, and then how you can access your Mac from another computer.
Turn on Remote Login (SSH and SFTP)
These steps explain how you can turn on Remote Login. Follow these steps on the Mac you want to access remotely.
- Click the Apple menu and then System Settings on your Mac.
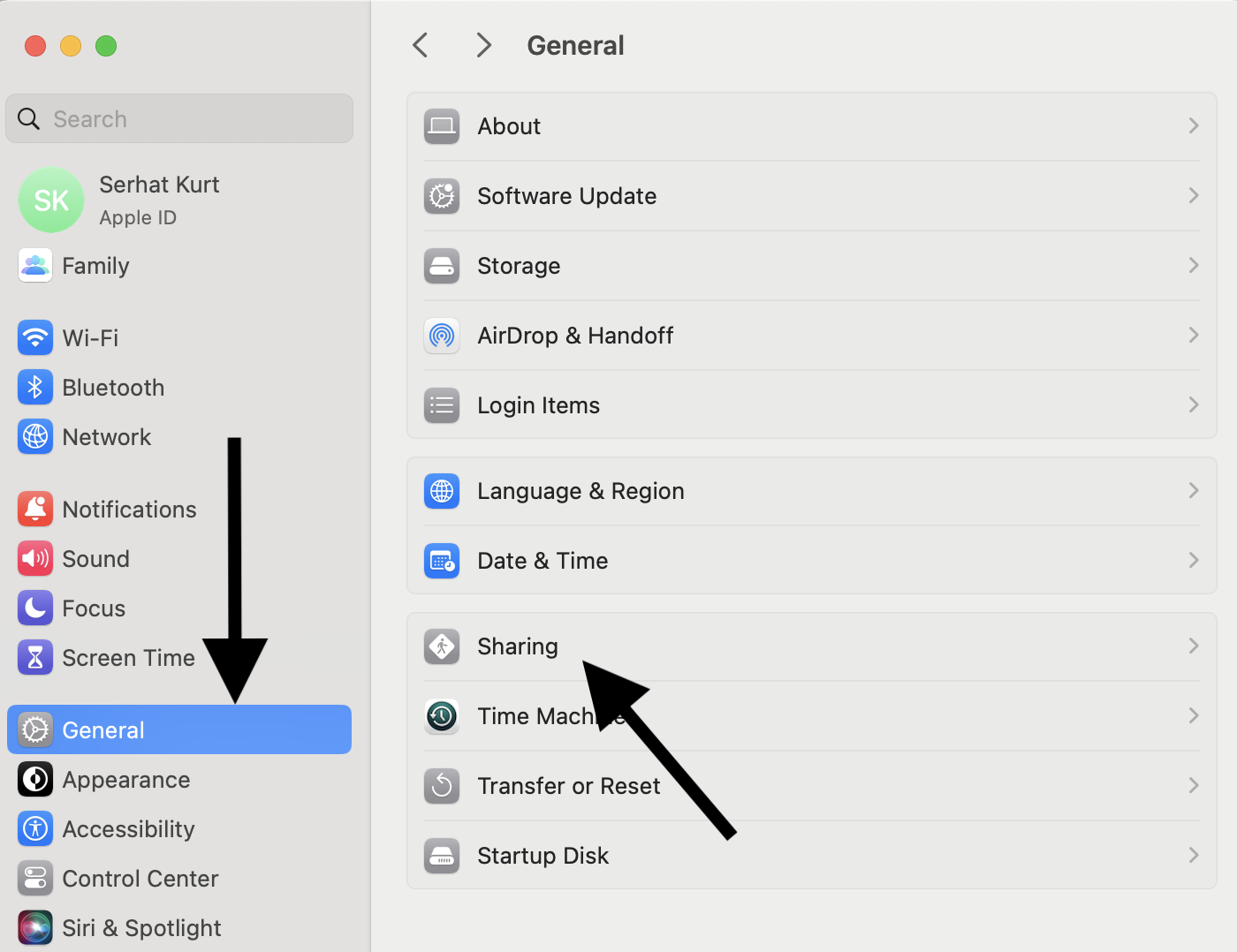
- From the left sidebar, click General, then select Sharing.
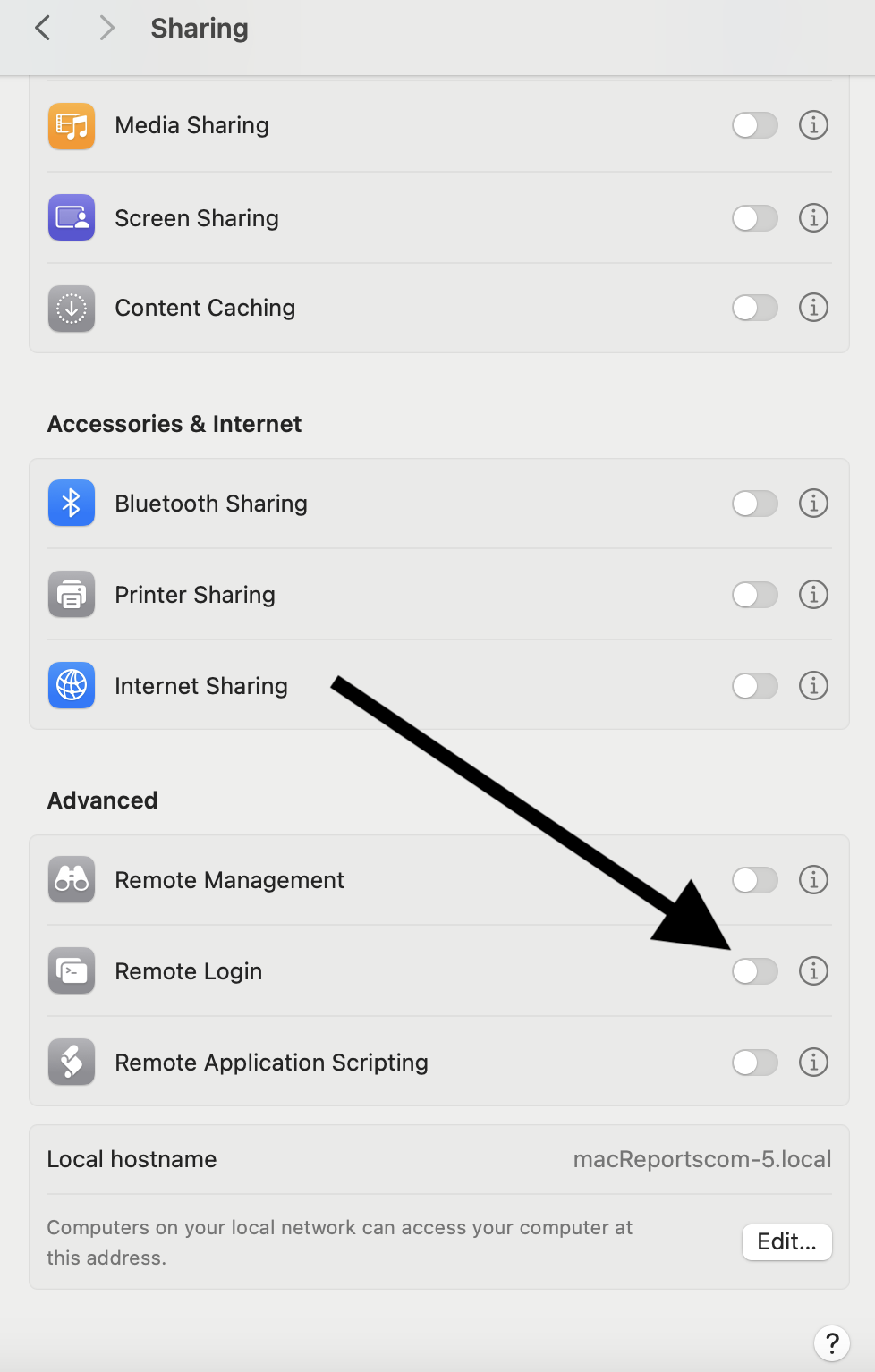
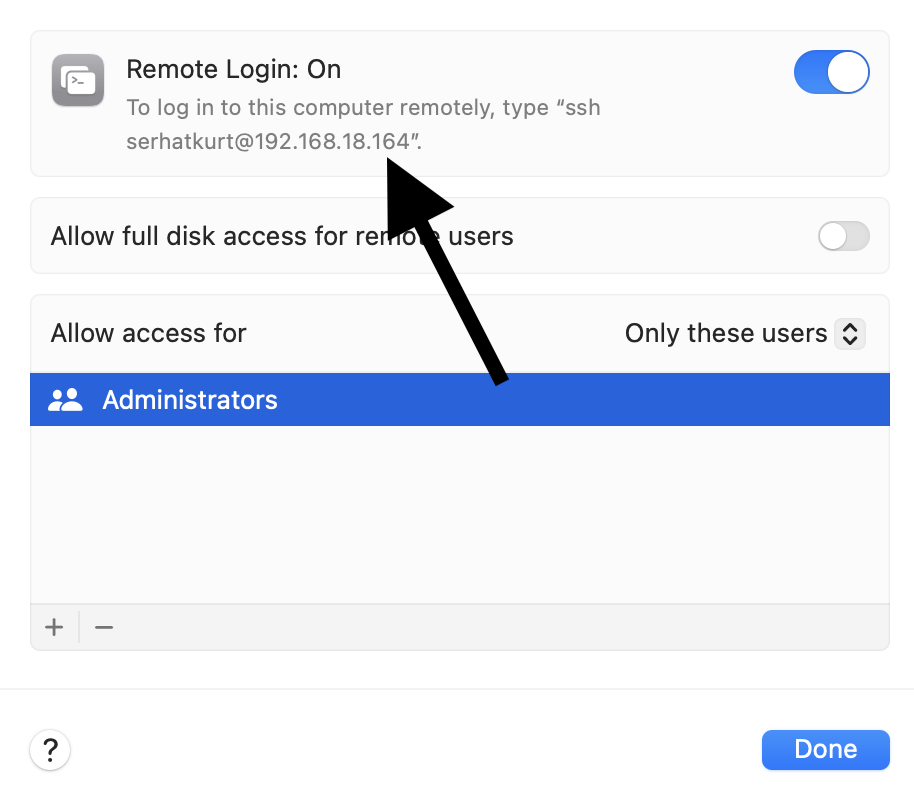
- Scroll down and find the Advanced section. Then, toggle on the Remote Login option.
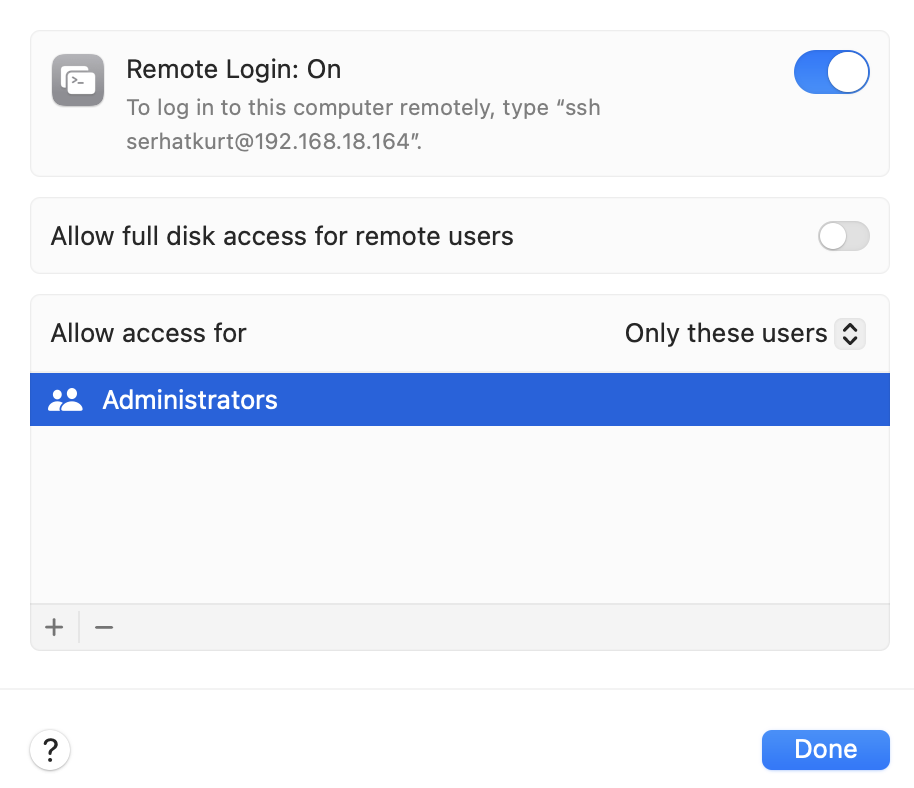
Now, you have enabled SSH and SFTP access to the computer. You can customize the access settings further by clicking the (i) button next to the on/off toggle. You can change the following settings:
- You can allow full disk access by selecting the Allow full disk access for remote users box.
- You can also choose which users can log in.
How to access a Mac via SSH
After enabling SSH, you can connect to that Mac via SSH. Here is how:
- Open Terminal or other SSH software.
- To initiate contact, you will need to use this format: ssh username@hostname or sftp username@hostname. If you go to the System Settings > General > Sharing and then click the (i) button next to Remote Login, you will see the username and hostname there, as you can see below:
If you try to access a Mac with Remote Login disabled, you will get a Connection Refused message.
Related articles