Wi-Fi Seems Slow, but Speed Test Shows it is Fine

There can be many reasons behind ‘slow’ internet speeds. It is frustrating to experience delays, buffering or seemingly slow speeds when you have paid for speedy Wi-Fi service in your home. There are Wi-Fi speed tests you can run, such as Ookla, to check if you are getting the Mbps you expect, but sometimes these test will look OK. If your internet seems slow or laggy, despite good bandwidth (high Mbps), you may be experiencing high latency; latency is basically the time it takes to transfer data from one place to another.
Latency can be especially problematic for real-time activities like gaming and video chats. In this article, we will tell you how to figure out if latency is the cause of your slow internet and tell you some things you can do to reduce latency for your home Wi-Fi connections.
Definitions
First, we will give some definitions. While we used words like ‘speed’ and ‘slow’ to describe your internet in the above paragraphs, these aren’t quite accurate; What we really want to talk about are bandwidth or latency.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is how much information, or data, you can receive every second. It isn’t, technically, a measurement of speed, however, with lower bandwidth, information – such as a file you are downloading or a web page you are loading into your browser – may take longer to reach your computer in its entirety. Since you wait longer for something to happen, you naturally describe your internet as slower.
Latency
Latency is basically a delay in information transfer. It always takes some amount of time for things (data) to get from one place to another, so when someone talks about latency, they usually mean lag, or high latency – things taking longer than they should to get from one place to another.
Ping
Ping is a way to measure latency. Ping tests measure how long it takes for data to be sent out to, and then return from, a specific location.
How to Determine if Latency is a Problem
You can measure latency by doing a ping test. Ok, fine, but what’s a good ping? Well, there is no one answer to that question, however, what you can do is compare pings. You can make a few changes – at your home – and test the effect of the changes. This can help you decide what you might do to reduce latency. Basically, if you notice a pause when loading a web page, or if you have to wait for the movie you’re streaming to buffer, or if your online games are laggy, then you are experiencing higher latency than you want. The Ping and Traceroute tests can let you see the effect of any changes you make.
Tests
There are a couple of tests you can run to check latency, ping and traceroute. Ping will tell you how long it takes to send and receive data from an address (server, modem, router, etc.). Traceroute will tell you times to send and receive data from each stop along the data’s route; Your data’s route likely involves: your router, your modem, and a few servers along the way to its destination.
To run ping or traceroute, you will use Terminal.
- To open Terminal, first open Finder, then go to the top menu and select Go, then Utilities. Double-click on Terminal.
Traceroute
- On the command line, type: traceroute [server name]. For example, type: traceroute google.com.
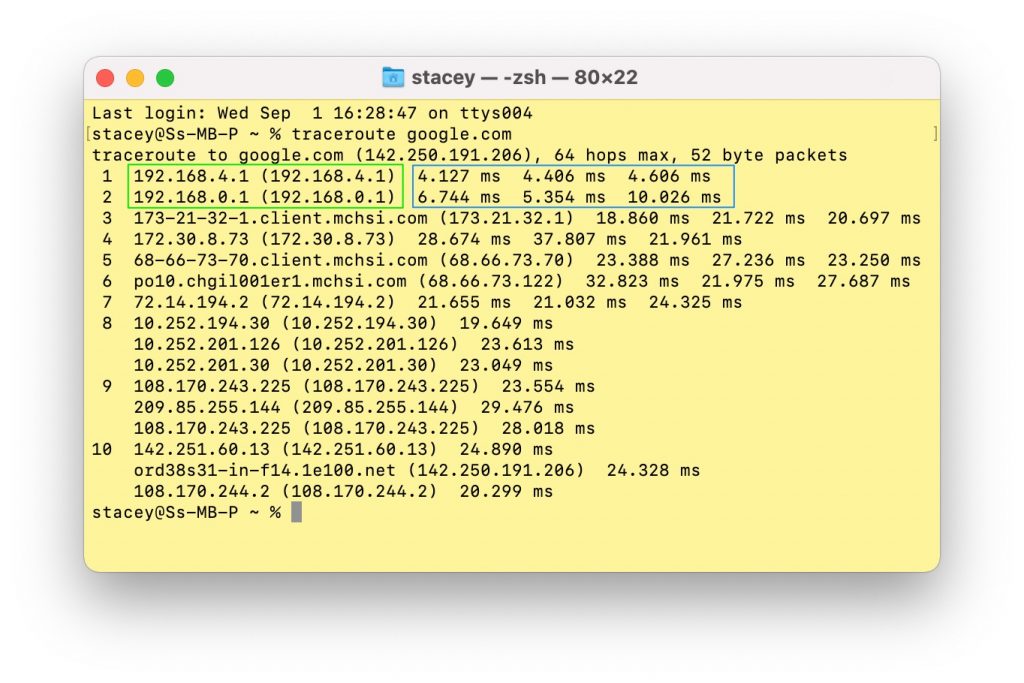
To find your modem and router address, you can run traceroute on any site. The first stop will be your router, the next will be your modem, then on to the outside world. In the following screenshot, the addresses of the first two stops – router, then modem – are outlined in green. The ping times are outlined in blue.
Ping
- On the command line, type: ping -c 50 [server name], then press Return (Enter). For example, you can type: ping -c 50 google.com. The number 50 is the number of pings; You can change it to whatever you like.
- You will see output listing ping times. The final output will also tell you the min/ave/max/stddev for those times which will be a nice summary you can use for comparison.
To check the latency within your home, you can ping your modem and/or your router. Modems usually have an address like 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1, so to ping your modem, you would type: ping -c 50 192.168.0.1. You can look for your modem’s documentation, look online, or do traceroute to find the address for both your modem and your router.
Other Tests
Other tests that can come in handy when trying to identify the cause of ‘slow’ or laggy internet are:
- The Ookla test at speedtest.net will test your bandwidth (Mbs).
- The free Netspot app can tell you many things about your Wi-Fi; It will show you all the Wi-Fi signals near you – in your home and likely some of your neighbors too, the signal strengths of all those Wi-Fi signals, the amount of noise in the signals and what channel each Wi-Fi signal is using.
How to Reduce Latency
There are a few changes you can make in your home to reduce latency.
Wired Connection
While for many, this may not be an ideal solution, using a wired, ethernet, connection to your modem/router is one guaranteed way to reduce latency. It is inexpensive and simple enough to implement; The drawback is that, for many people, their modem is located in another room or on the other side of their house.
Router Placement
Having your computer close to your Wi-Fi router should reduce your latency. If your modem/router is located somewhat far from where you use your computer, or if there are signal-blocking obstructions between them, you can either consider moving the modem/router or moving your work area.
Router Settings and Updates
It might be worth it to check your modem/router’s settings and to check for any updates. How to access the settings varies among manufacturers, and if you are renting your modem/router from your service provider, you may need to call them. Assuming you own your equipment, you can check the documentation that came with your modem/router, or do an internet search for how to access your modem/router’s settings. If you have changed the default password in the past, you will need that too.
New Modem/Router
If your equipment is older – you might compare the specs with what’s available now – you should maybe consider an equipment upgrade.
Mesh Wi-Fi and Signal Boosters
All of these systems designed to extend the range of your Wi-Fi will add some degree of latency – some worse than others. They are best used when the Wi-Fi signal strength is inadequate, which will likely be reflected in the Mbs you see when running a speed test. However, if you know your signal strength is low or unreliable, one of these systems may help.
Mesh Wi-Fi
Mesh Wi-Fi systems are a good way to extend your Wi-Fi signal to regions of your home that are not close to your modem. Mesh Wi-Fi replaces your current Wi-Fi router with a set, usually 2 or 3, devices that will all work together to provide Wi-Fi coverage for your home.
Wi-Fi Booster
One type of Wi-Fi booster (repeater, extender) works by placing a unit in between your router and your computer; The booster retransmits the Wi-Fi signal so that it reaches farther than the original signal from your router. The downside to these is the added latency because of the extra stop along your data’s route and the reduced signal strength being transmitted by the booster. Another type uses your electrical wiring; One unit is plugged into your router and an electrical outlet and another is plugged in near your computer.
More General Wi-Fi Issues
If your Wi-Fi issues go beyond latency, or if you want to check your Mac to make sure there is nothing else affecting your perceived internet speed, there are several tips in our article: Wi-Fi Not Working after Update.
Related Articles: