macOS: How to Flush DNS
Flushing DNS may be necessary in some situations to ensure that your Mac has the most up-to-date information about domain names and their corresponding IP addresses. Network administrators do this often to refresh their connections. Flushing the DNS means removing the DNS cache. More specifically, it is the process of clearing or resetting the DNS resolver cache on your Mac.
Why flush DNS?
Here are some examples:
- Flushing DNS may be a good troubleshooting step if you are unable to access a certain website.
- If you have a website and you changed its DNS servers, flushing the DNS cache ensures that your computer doesn’t continue to use the old, cached IP address and instead retrieves the new DNS servers.
- Flushing DNS will also increase your privacy by removing traces of the websites you’ve visited at the DNS level.
Steps to clear & reset DNS on your Mac
- Open Terminal on your Mac. You can use Spotlight to launch it or go to the Utilities folder inside the Applications folder.
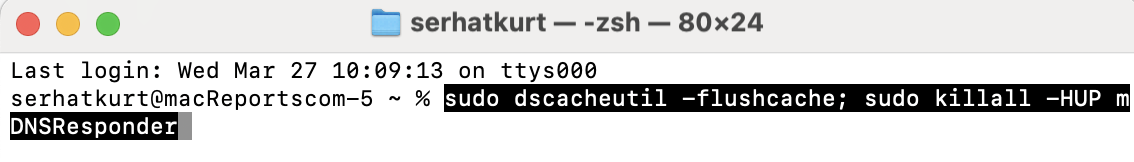
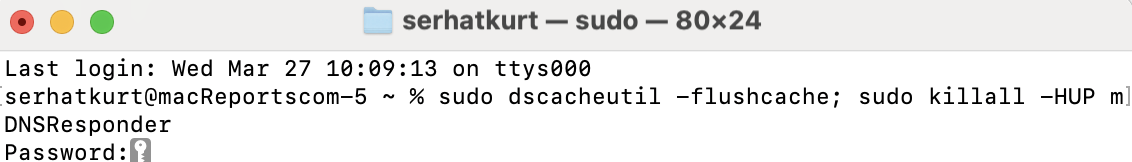
- Copy the following code, paste it into the Terminal app and hit enter; see the screenshot below:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder- Terminal will ask for your password. Enter it. Then, your DNS will be cleared. You are done.
Please note that flushing DNS will not erase your browsing history or Internet cookies.
Related articles